Satellites Formerly Orbiting Earth on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into
 In the context of activities planned for the
In the context of activities planned for the
 While Canada was the third country to build a satellite which was launched into space, it was launched aboard an
While Canada was the third country to build a satellite which was launched into space, it was launched aboard an
 Most satellites use chemical or
Most satellites use chemical or
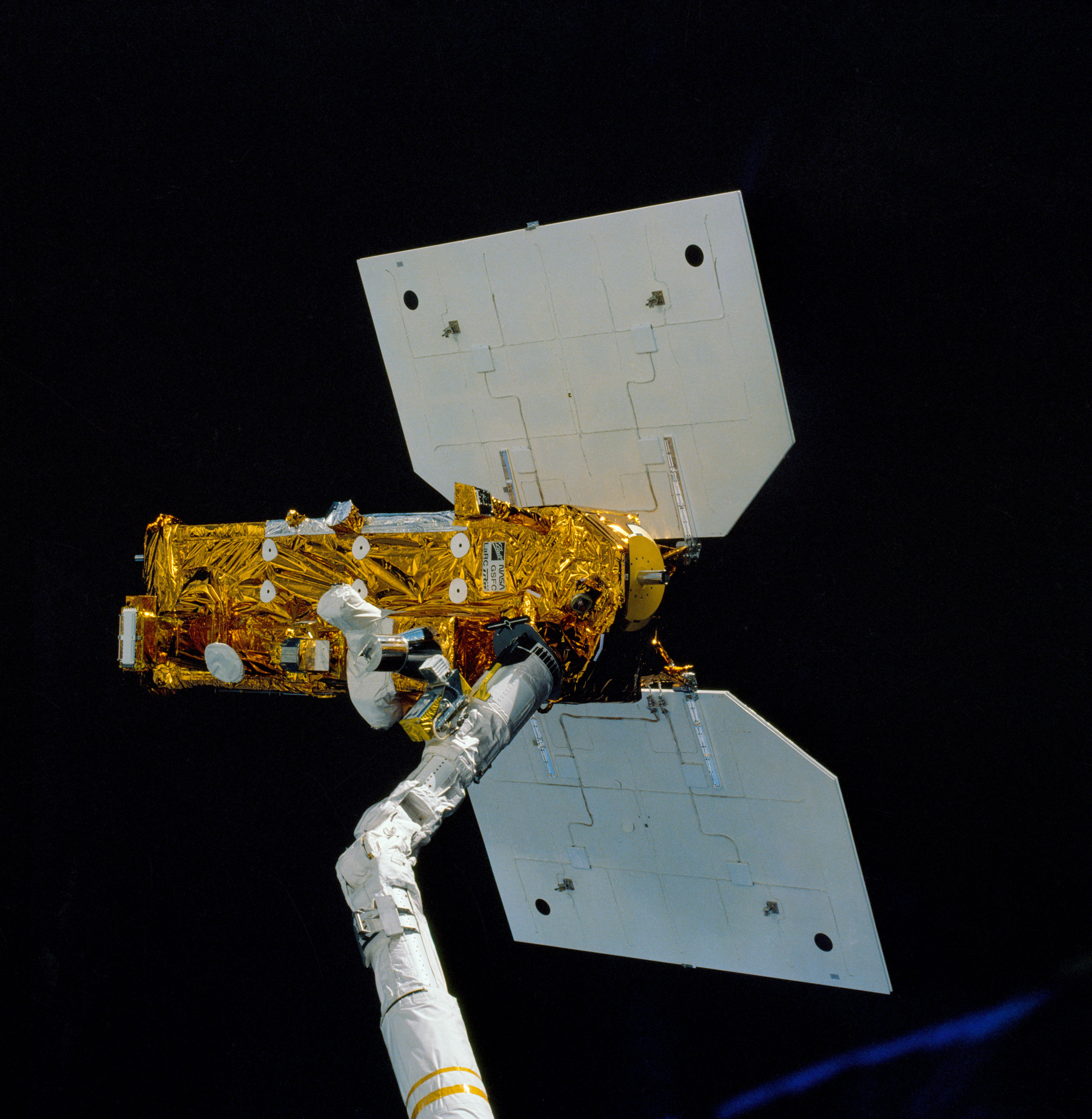 Earth observation satellites is designed to monitor and survey the Earth, called
Earth observation satellites is designed to monitor and survey the Earth, called

EO Portal directory
{{DEFAULTSORT:Earth Observation Satellite Earth observation satellites, Satellites by type Satellite imagery Satellites, Articles containing video clips Spacecraft Soviet inventions
 A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as a p ...
in outer space
Outer space, commonly shortened to space, is the expanse that exists beyond Earth and its atmosphere and between celestial bodies. Outer space is not completely empty—it is a near-perfect vacuum containing a low density of particles, pred ...
. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For electric utility, utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its Electricity delivery, delivery (Electric power transmi ...
system for equipment on board, such as solar panel
A solar cell panel, solar electric panel, photo-voltaic (PV) module, PV panel or solar panel is an assembly of photovoltaic solar cells mounted in a (usually rectangular) frame, and a neatly organised collection of PV panels is called a photo ...
s or radioisotope thermoelectric generator
A radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG, RITEG), sometimes referred to as a radioisotope power system (RPS), is a type of nuclear battery that uses an array of thermocouples to convert the heat released by the decay of a suitable radioacti ...
s (RTGs). Most satellites also have a method of communication to ground station
A ground station, Earth station, or Earth terminal is a terrestrial radio station designed for extraplanetary telecommunication with spacecraft (constituting part of the ground segment of the spacecraft system), or reception of radio waves fro ...
s, called transponders
In telecommunications, a transponder is a device that, upon receiving a signal, emits a different signal in response. The term is a blend of ''transmitter'' and ''responder''.
In air navigation or radio frequency identification, a flight trans ...
. Many satellites use a standardized bus to save cost and work, the most popular of which is small CubeSat
A CubeSat is a class of miniaturized satellite based around a form factor consisting of cubes. CubeSats have a mass of no more than per unit, and often use commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) components for their electronics and structure. CubeSats ...
s. Similar satellites can work together as a group, forming constellations
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the earliest constellation ...
. Because of the high launch cost
Space launch market competition is the manifestation of market forces in the launch service provider business. In particular it is the trend of competitive dynamics among payload transport capabilities at diverse prices having a greater influe ...
to space, satellites are designed to be as lightweight and robust as possible. Most communication satellites are radio relay stations in orbit and carry dozens of transponders, each with a bandwidth of tens of megahertz.
Satellites are placed from the surface to orbit by launch vehicle
A launch vehicle or carrier rocket is a rocket designed to carry a payload (spacecraft or satellites) from the Earth's surface to outer space. Most launch vehicles operate from a launch pad, launch pads, supported by a missile launch contro ...
s, high enough to avoid orbital decay
Orbital decay is a gradual decrease of the distance between two orbiting bodies at their closest approach (the periapsis) over many orbital periods. These orbiting bodies can be a planet and its satellite, a star and any object orbiting it, or ...
by the atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ...
. Satellites can then change or maintain the orbit by propulsion
Propulsion is the generation of force by any combination of pushing or pulling to modify the translational motion of an object, which is typically a rigid body (or an articulated rigid body) but may also concern a fluid. The term is derived from ...
, usually by chemical
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., wi ...
or ion thruster
An ion thruster, ion drive, or ion engine is a form of electric propulsion used for spacecraft propulsion. It creates thrust by accelerating ions using electricity.
An ion thruster ionizes a neutral gas by extracting some electrons out of a ...
s. In 2018, about 90% of satellites orbiting Earth are in low Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never mor ...
or geostationary orbit
A geostationary orbit, also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit''Geostationary orbit'' and ''Geosynchronous (equatorial) orbit'' are used somewhat interchangeably in sources. (GEO), is a circular geosynchronous orbit in altitud ...
; geostationary means the satellites stay still at the sky. Some imaging satellites chose a Sun-synchronous orbit
A Sun-synchronous orbit (SSO), also called a heliosynchronous orbit, is a nearly polar orbit around a planet, in which the satellite passes over any given point of the planet's surface at the same local mean solar time. More technically, it is ...
because they can scan the entire globe with similar lighting. As the number of satellites and space debris
Space debris (also known as space junk, space pollution, space waste, space trash, or space garbage) are defunct human-made objects in space—principally in Earth orbit—which no longer serve a useful function. These include derelict spacecr ...
around Earth increases, the collision threat is becoming more severe. A small number of satellites orbit other bodies (such as the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
, Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury (planet), Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Mars (mythology), Roman god of war. Mars is a terr ...
, and the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
) or many bodies at once (two for a halo orbit
A halo orbit is a periodic, three-dimensional orbit near one of the L1, L2 or L3 Lagrange points in the three-body problem of orbital mechanics. Although a Lagrange point is just a point in empty space, its peculiar characteristic is that it ca ...
, three for a Lissajous orbit
In orbital mechanics, a Lissajous orbit (), named after Jules Antoine Lissajous, is a quasi-periodic orbital trajectory that an object can follow around a Lagrangian point of a three-body system without requiring any propulsion. Lyapunov orbits ...
).
Earth observation satellite
An Earth observation satellite or Earth remote sensing satellite is a satellite used or designed for Earth observation (EO) from orbit, including spy satellites and similar ones intended for non-military uses such as environmental monitoring, me ...
s gather information for reconnaissance
In military operations, reconnaissance or scouting is the exploration of an area by military forces to obtain information about enemy forces, terrain, and other activities.
Examples of reconnaissance include patrolling by troops (skirmisher ...
, mapping, monitoring the weather, ocean, forest, etc. Space telescope
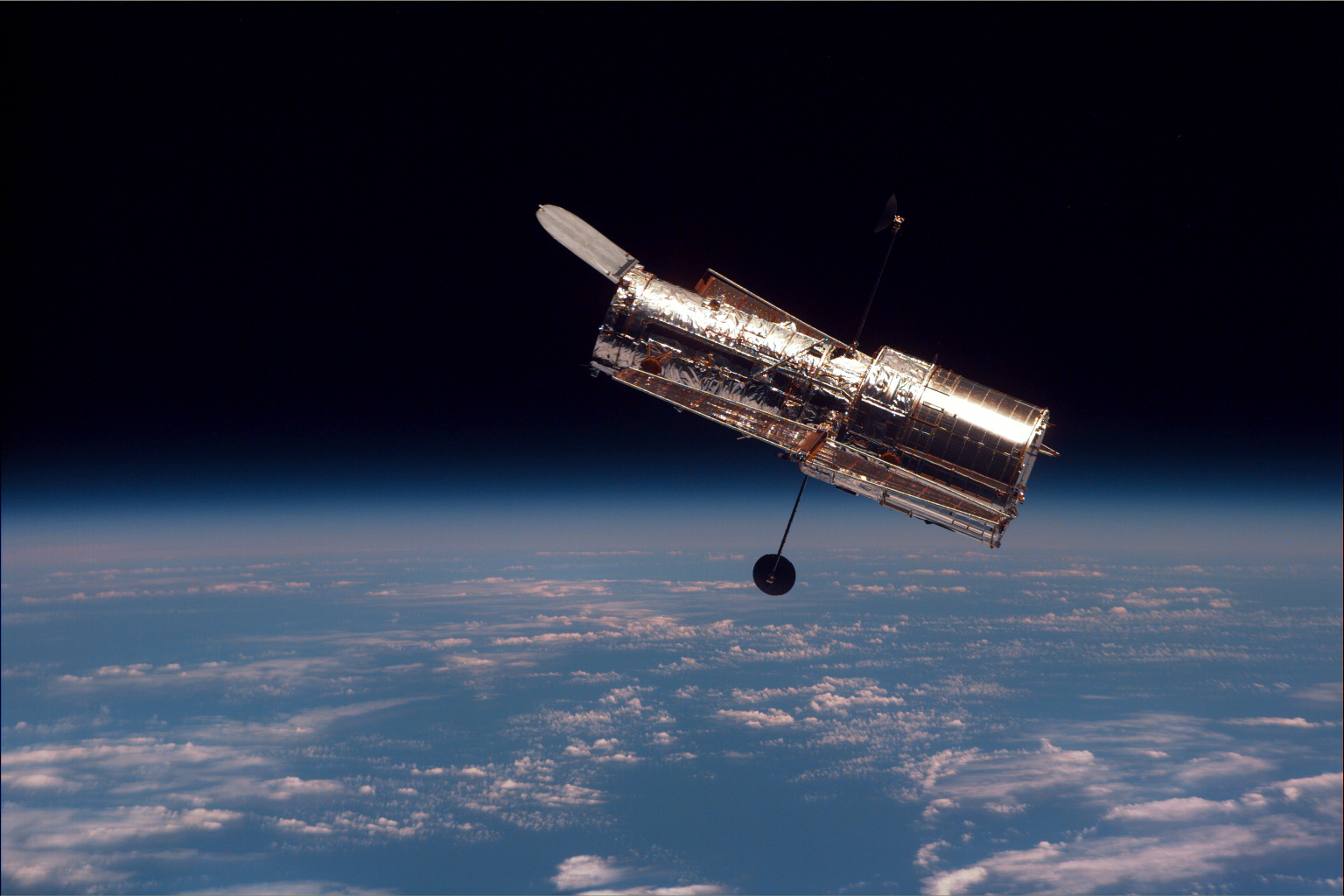
A space telescope or space observatory is a telescope in outer space used to observe astronomical objects. Suggested by Lyman Spitzer in 1946, the first operational telescopes were the American Orbiting Astronomical Observatory, OAO-2 launched ...
s take advantage of outer space's near perfect vacuum to observe objects with the entire electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of frequencies (the spectrum) of electromagnetic radiation and their respective wavelengths and photon energies.
The electromagnetic spectrum covers electromagnetic waves with frequencies ranging from ...
. Because satellites can see a large portion of the Earth at once, communications satellites
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. C ...
can relay information to remote places. The signal delay from satellites and their orbit's predictability are used in satellite navigation
A satellite navigation or satnav system is a system that uses satellites to provide autonomous geo-spatial positioning. It allows satellite navigation devices to determine their location (longitude, latitude, and altitude/elevation) to high pr ...
systems, such as GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a Radionavigation-satellite service, satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of t ...
. Space probe
A space probe is an artificial satellite that travels through space to collect scientific data. A space probe may orbit Earth; approach the Moon; travel through interplanetary space; flyby, orbit, or land or fly on other planetary bodies; or ent ...
s are satellites designed for robotic space exploration
Space exploration is the use of astronomy and space technology to explore outer space. While the exploration of space is carried out mainly by astronomers with telescopes, its physical exploration though is conducted both by robotic spacec ...
outside of Earth, and space station
A space station is a spacecraft capable of supporting a human crew in orbit for an extended period of time, and is therefore a type of space habitat. It lacks major propulsion or landing systems. An orbital station or an orbital space station i ...
s are in essence crewed satellites.
The first artificial satellite to be launched into the Earth's orbit was the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
's Sputnik 1
Sputnik 1 (; see § Etymology) was the first artificial Earth satellite. It was launched into an elliptical low Earth orbit by the Soviet Union on 4 October 1957 as part of the Soviet space program. It sent a radio signal back to Earth for t ...
, on 4 October 1957.
History
Early proposals
The first published mathematical study of the possibility of an artificial satellite wasNewton's cannonball
Newton's cannonball was a thought experiment Isaac Newton used to hypothesize that the force of gravity was universal, and it was the key force for planetary motion. It appeared in his posthumously published 1728 work ''De mundi systemate'' (als ...
, a thought experiment by Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a "natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the grea ...
to explain the motion of natural satellite
A natural satellite is, in the most common usage, an astronomical body that orbits a planet, dwarf planet, or small Solar System body (or sometimes another natural satellite). Natural satellites are often colloquially referred to as ''moons'' ...
s, in his ''Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica
(English: ''Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy'') often referred to as simply the (), is a book by Isaac Newton that expounds Newton's laws of motion and his law of universal gravitation. The ''Principia'' is written in Latin and ...
'' (1687). The first fictional depiction of a satellite being launched into orbit was a short story
A short story is a piece of prose fiction that typically can be read in one sitting and focuses on a self-contained incident or series of linked incidents, with the intent of evoking a single effect or mood. The short story is one of the oldest ...
by Edward Everett Hale
Edward Everett Hale (April 3, 1822 – June 10, 1909) was an American author, historian, and Unitarian minister, best known for his writings such as "The Man Without a Country", published in ''Atlantic Monthly'', in support of the Union dur ...
, "The Brick Moon
"The Brick Moon" is a novella by American writer Edward Everett Hale, published serially in ''The Atlantic Monthly'' starting in 1869. It is a work of speculative fiction containing the first known depiction of the launch of an artificial satel ...
" (1869). The idea surfaced again in Jules Verne
Jules Gabriel Verne (;''Longman Pronunciation Dictionary''. ; 8 February 1828 – 24 March 1905) was a French novelist, poet, and playwright. His collaboration with the publisher Pierre-Jules Hetzel led to the creation of the ''Voyages extraor ...
's ''The Begum's Fortune
''The Begum's Fortune'' (french: Les Cinq cents millions de la Bégum, literally "the 500 millions of the begum"), also published as ''The Begum's Millions'', is an 1879 novel by Jules Verne, with some utopian elements and other elements that seem ...
'' (1879).
In 1903, Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Eduardovich Tsiolkovsky (russian: Константи́н Эдуа́рдович Циолко́вский , , p=kənstɐnʲˈtʲin ɪdʊˈardəvʲɪtɕ tsɨɐlˈkofskʲɪj , a=Ru-Konstantin Tsiolkovsky.oga; – 19 September 1935) ...
(1857–1935) published ''Exploring Space Using Jet Propulsion Devices'', which is the first academic treatise on the use of rocketry to launch spacecraft. He calculated the orbital speed
In gravitationally bound systems, the orbital speed of an astronomical body or object (e.g. planet, moon, artificial satellite, spacecraft, or star) is the speed at which it orbits around either the barycenter or, if one body is much more massi ...
required for a minimal orbit, and that a multi-stage rocket
A multistage rocket or step rocket is a launch vehicle that uses two or more rocket ''stages'', each of which contains its own engines and propellant. A ''tandem'' or ''serial'' stage is mounted on top of another stage; a ''parallel'' stage is ...
fueled by liquid propellant
A propellant (or propellent) is a mass that is expelled or expanded in such a way as to create a thrust or other motive force in accordance with Newton's third law of motion, and "propel" a vehicle, projectile, or fluid payload. In vehicles, the e ...
s could achieve this.
Herman Potočnik explored the idea of using orbiting spacecraft for detailed peaceful and military observation of the ground in his 1928 book, ''The Problem of Space Travel''. He described how the special conditions of space could be useful for scientific experiments. The book described geostationary
A geostationary orbit, also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit''Geostationary orbit'' and ''Geosynchronous (equatorial) orbit'' are used somewhat interchangeably in sources. (GEO), is a circular geosynchronous orbit in altitude ...
satellites (first put forward by Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Eduardovich Tsiolkovsky (russian: Константи́н Эдуа́рдович Циолко́вский , , p=kənstɐnʲˈtʲin ɪdʊˈardəvʲɪtɕ tsɨɐlˈkofskʲɪj , a=Ru-Konstantin Tsiolkovsky.oga; – 19 September 1935) ...
) and discussed communication between them and the ground using radio, but fell short of the idea of using satellites for mass broadcasting and as telecommunications relays.
In a 1945 ''Wireless World
''Electronics World'' (''Wireless World'', founded in 1913, and in September 1984 renamed ''Electronics & Wireless World'') is a technical magazine in electronics and RF engineering aimed at professional design engineers. It is produced monthly in ...
'' article, the English science fiction writer Arthur C. Clarke described in detail the possible use of communications satellite
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. C ...
s for mass communications. He suggested that three geostationary satellites would provide coverage over the entire planet.
In May 1946, the United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Signal ...
's Project RAND
The RAND Corporation (from the phrase "research and development") is an American nonprofit global policy think tank created in 1948 by Douglas Aircraft Company to offer research and analysis to the United States Armed Forces. It is financed ...
released the Preliminary Design of an Experimental World-Circling Spaceship
The Preliminary Design of an Experimental World-Circling Spaceship was a 1946 proposal by Project RAND for a United States satellite program. Robert M. Salter, Jack Lipp and one other person at RAND served as the editors of the report.
The Prelimi ...
, which stated "A satellite vehicle with appropriate instrumentation can be expected to be one of the most potent scientific tools of the Twentieth Century." The United States had been considering launching orbital satellites since 1945 under the Bureau of Aeronautics
The Bureau of Aeronautics (BuAer) was the U.S. Navy's material-support organization for naval aviation from 1921 to 1959. The bureau had "cognizance" (''i.e.'', responsibility) for the design, procurement, and support of naval aircraft and relate ...
of the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
. Project RAND eventually released the report, but considered the satellite to be a tool for science, politics, and propaganda, rather than a potential military weapon.
In 1946, American theoretical astrophysicist Lyman Spitzer
Lyman Spitzer Jr. (June 26, 1914 – March 31, 1997) was an American theoretical physicist, astronomer and mountaineer. As a scientist, he carried out research into star formation, plasma physics, and in 1946, conceived the idea of telescop ...
proposed an orbiting space telescope
A space telescope or space observatory is a telescope in outer space used to observe astronomical objects. Suggested by Lyman Spitzer in 1946, the first operational telescopes were the American Orbiting Astronomical Observatory, OAO-2 launched ...
.
In February 1954, Project RAND released "Scientific Uses for a Satellite Vehicle", by R. R. Carhart. This expanded on potential scientific uses for satellite vehicles and was followed in June 1955 with "The Scientific Use of an Artificial Satellite", by H. K. Kallmann and W. W. Kellogg.
First satellites
 In the context of activities planned for the
In the context of activities planned for the International Geophysical Year
The International Geophysical Year (IGY; french: Année géophysique internationale) was an international scientific project that lasted from 1 July 1957 to 31 December 1958. It marked the end of a long period during the Cold War when scientific ...
(1957–1958), the White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. It is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington, D.C., and has been the residence of every U.S. president since John Adams in 1800. ...
announced on 29 July 1955 that the U.S. intended to launch satellites by the spring of 1958. This became known as Project Vanguard
Project Vanguard was a program managed by the United States Navy Naval Research Laboratory (NRL), which intended to launch the first artificial satellite into low Earth orbit using a Vanguard rocket. as the launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral ...
. On 31 July, the Soviet Union announced its intention to launch a satellite by the fall of 1957.
The first artificial satellite was Sputnik 1
Sputnik 1 (; see § Etymology) was the first artificial Earth satellite. It was launched into an elliptical low Earth orbit by the Soviet Union on 4 October 1957 as part of the Soviet space program. It sent a radio signal back to Earth for t ...
, launched by the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
on 4 October 1957 under the Sputnik program
Sputnik (Спутник, Russian for "satellite"NOTE: The Russian word "sputnik" can have many meanings: "satellite", "travelling companion", "fellow traveller", etc. However, in astronomy, it means only "satellite".) is a spacecraft launched ...
, with Sergei Korolev
Sergei Pavlovich Korolev (russian: Сергей Павлович Королёв, Sergey Pavlovich Korolyov, sʲɪrˈɡʲej ˈpavləvʲɪtɕ kərɐˈlʲɵf, Ru-Sergei Pavlovich Korolev.ogg; ukr, Сергій Павлович Корольов, ...
as chief designer. Sputnik 1 helped to identify the density of high atmospheric layers
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for ...
through measurement of its orbital change and provided data on radio-signal distribution in the ionosphere
The ionosphere () is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about to above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an ...
. The unanticipated announcement of Sputnik 1's success precipitated the Sputnik crisis
The Sputnik crisis was a period of public fear and anxiety in Western nations about the perceived technological gap between the United States and Soviet Union caused by the Soviets' launch of ''Sputnik 1'', the world's first artificial satelli ...
in the United States and ignited the so-called Space Race within the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
.
Sputnik 2
Sputnik 2 (, russian: Спутник-2, ''Satellite 2''), or Prosteyshiy Sputnik 2 (PS-2, russian: Простейший Спутник 2, italic=yes, ''Simplest Satellite 2'') was the second spacecraft launched into Earth orbit, on 3 November 195 ...
was launched on 3 November 1957 and carried the first living passenger into orbit, a dog named Laika
Laika (russian: link=no, Лайка; – 3 November 1957) was a Soviet space dog who was one of the first animals in space and the first to orbit the Earth. A stray mongrel from the streets of Moscow, she flew aboard the Sputnik 2 spacecra ...
.
In early 1955, after pressure by the American Rocket Society
The American Rocket Society (ARS) began its existence on , under the name of the American Interplanetary Society. It was founded by science fiction writers G. Edward Pendray, David Lasser, Laurence Manning, Nathan Schachner, and others. Pendray ...
, the National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National I ...
, and the International Geophysical Year, the Army and Navy were working on Project Orbiter with two competing programs. The army used the Jupiter C rocket, while the civilian–Navy program used the Vanguard rocket
The Vanguard rocket was intended to be the first launch vehicle the United States would use to place a satellite into orbit. Instead, the Sputnik crisis caused by the surprise launch of Sputnik 1 led the U.S., after the failure of Vanguard TV-3 ...
to launch a satellite. Explorer 1
Explorer 1 was the first satellite launched by the United States in 1958 and was part of the U.S. participation in the International Geophysical Year (IGY). The mission followed the first two satellites the previous year; the Soviet Union's ...
became the United States' first artificial satellite, on 31 January 1958. The information sent back from its radiation detector led to the discovery of the Earth's Van Allen radiation belts. The TIROS-1
TIROS-1 (or TIROS-A) was the first full-scale weather satellite (the Vanguard 2 satellite was the first experimental/prototype weather satellite), the first of a series of Television Infrared Observation Satellites placed in low Earth orbit.
Pr ...
spacecraft, launched on April 1, 1960, as part of NASA's Television Infrared Observation Satellite
TIROS, or Television InfraRed Observation Satellite, is a series of early weather satellites launched by the United States, beginning with TIROS-1 in 1960. TIROS was the first satellite that was capable of remote sensing of the Earth, enablin ...
(TIROS) program, sent back the first television footage of weather patterns to be taken from space.
In June 1961, three and a half years after the launch of Sputnik 1, the United States Space Surveillance Network
The United States Space Surveillance Network (SSN) detects, tracks, catalogs and identifies artificial objects orbiting Earth, e.g. active/inactive satellites, spent rocket bodies, or fragmentation debris. The system is the responsibility of Uni ...
cataloged 115 Earth-orbiting satellites.
Early satellites were built to unique designs. With advancements in technology, multiple satellites began to be built on single model platforms called satellite bus
A satellite bus (or spacecraft bus) is the main body and structural component of a satellite or spacecraft, in which the payload and all scientific instruments are held.
Bus-derived satellites are opposed to specially produced satellites. Bus-d ...
es. The first standardized satellite bus design was the HS-333
In 1970, Hughes Aircraft Company (HAC) Space and Communications Group offered the first standardized satellite: the HS 333 design. A spinning satellite, it was based on previous one-design satellites like Intelsat I. HAC built eight of these 300 ...
geosynchronous
A geosynchronous orbit (sometimes abbreviated GSO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an orbital period that matches Earth's rotation on its axis, 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds (one sidereal day). The synchronization of rotation and orbital ...
(GEO) communication satellite
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. C ...
launched in 1972. Begun in 1997, FreeFlyer is a commercial off-the-shelf software application for satellite mission analysis, design, and operations.
Later development
 While Canada was the third country to build a satellite which was launched into space, it was launched aboard an
While Canada was the third country to build a satellite which was launched into space, it was launched aboard an American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
rocket from an American spaceport. The same goes for Australia, who launched first satellite involved a donated U.S. Redstone rocket and American support staff as well as a joint launch facility with the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
. The first Italian satellite San Marco 1
San Marco 1, also known as San Marco A, was the first Italian satellite. Built in-house by the Italian Space Research Commission ( it, Commissione per le Ricerche Spaziali, CRS) on behalf of the National Research Council, it was the first of five ...
launched on 15 December 1964 on a U.S. Scout rocket
The Scout family of rockets were American launch vehicles designed to place small satellites into orbit around the Earth. The Scout multistage rocket was the first orbital launch vehicle to be entirely composed of Solid rocket, solid fuel stages. ...
from Wallops Island
Wallops Island is a island in Accomack County, Virginia, part of the Virginia Barrier Islands that stretch along the eastern seaboard of the United States of America. It is just south of Chincoteague Island, a popular tourist destination.
W ...
(Virginia, United States) with an Italian launch team trained by NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeeding t ...
. By similar occasions, almost all further first national satellites was launched by foreign rockets.
After the late 2010s, and especially after the advent and operational fielding of large satellite internet constellation
A satellite internet constellation is a constellation of artificial satellites providing satellite internet service. In particular, the term has come to refer to a new generation of very large constellations (sometimes referred to as a megaco ...
s—where on-orbit active satellites more than doubled over a period of five years—the companies building the constellations began to propose regular planned deorbiting of the older satellites that reach end of life, as a part of the regulatory process of obtaining a launch license. The largest artificial satellite ever is the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA ...
.
By the early 2000s, and particularly after the advent of CubeSat
A CubeSat is a class of miniaturized satellite based around a form factor consisting of cubes. CubeSats have a mass of no more than per unit, and often use commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) components for their electronics and structure. CubeSats ...
s and increased launches of microsats—frequently launched to the lower altitudes of low Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never mor ...
(LEO)—satellites began to more frequently be designed to demise, or breakup and burnup entirely in the atmosphere.
For example, SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) is an American spacecraft manufacturer, launcher, and a satellite communications corporation headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the stated goal of ...
Starlink
Starlink is a satellite internet constellation operated by SpaceX, providing satellite Internet access coverage to 45 countries. It also aims for global mobile phone service after 2023. SpaceX started launching Starlink satellites in 2019. As ...
satellites, the first large satellite internet constellation to exceed 1000 active satellites on orbit in ~2020, are designed to be 100% demisable and burn up completely on atmospheric reentry at end of life, or in the event of an early satellite failure.
Components
Orbit and altitude control
 Most satellites use chemical or
Most satellites use chemical or ion propulsion
An ion thruster, ion drive, or ion engine is a form of electric propulsion used for spacecraft propulsion. It creates thrust by accelerating ions using electricity.
An ion thruster ionizes a neutral gas by extracting some electrons out of ...
to adjust or maintain their orbit, coupled with reaction wheel
A reaction wheel (RW) is used primarily by spacecraft for three-axis attitude control, and does not require rockets or external applicators of torque. They provide a high pointing accuracy, and are particularly useful when the spacecraft must be ...
s to control its three axis of rotation or attitude. Satellites close to Earth are affected the most by variations in the Earth's magnetic, gravitational field
In physics, a gravitational field is a model used to explain the influences that a massive body extends into the space around itself, producing a force on another massive body. Thus, a gravitational field is used to explain gravitational phenome ...
and the Sun's radiation pressure
Radiation pressure is the mechanical pressure exerted upon any surface due to the exchange of momentum between the object and the electromagnetic field. This includes the momentum of light or electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength that is a ...
; satellites that are further away are affected more by other bodies' gravitational field by the Moon and the Sun. Without orbit and orientation control, satellites in orbit will not be able to communicate with ground station
A ground station, Earth station, or Earth terminal is a terrestrial radio station designed for extraplanetary telecommunication with spacecraft (constituting part of the ground segment of the spacecraft system), or reception of radio waves fro ...
s on Earth.
Chemical thrusters on satellites usually use monopropellant
Monopropellants are propellants consisting of chemicals that release energy through exothermic chemical decomposition. The molecular bond energy of the monopropellant is released usually through use of a catalyst. This can be contrasted with biprop ...
(one-part) or bipropellant
The highest specific impulse chemical rockets use liquid propellants (liquid-propellant rockets). They can consist of a single chemical (a monopropellant) or a mix of two chemicals, called bipropellants. Bipropellants can further be divided into ...
(two-parts) that are hypergolic
A hypergolic propellant is a rocket propellant combination used in a rocket engine, whose components spontaneously ignite when they come into contact with each other.
The two propellant components usually consist of a fuel and an oxidizer. The ...
. Hypergolic means able to combust spontaneously in contact to each other or to a catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
. The most commonly used propellant mixtures on satellites are hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly toxic unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazine ...
-based monopropellant or monomethylhydrazine
Monomethylhydrazine (mono-methyl hydrazine, MMH) is a highly toxic, volatile hydrazine derivative with the chemical formula . It is used as a rocket propellant in bipropellant rocket engines because it is hypergolic with various oxidizers such as ...
–dinitrogen tetroxide
Dinitrogen tetroxide, commonly referred to as nitrogen tetroxide (NTO), and occasionally (usually among ex-USSR/Russia rocket engineers) as amyl, is the chemical compound N2O4. It is a useful reagent in chemical synthesis. It forms an equilibrium ...
bipropellant. Ion thrusters on satellites usually are Hall-effect thruster
In spacecraft propulsion, a Hall-effect thruster (HET) is a type of ion thruster in which the propellant is accelerated by an electric field. Hall-effect thrusters (based on the discovery by Edwin Hall) are sometimes referred to as Hall thruster ...
s, which generate thrust by accelerating positive ions
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
through a negatively-charged grid. Ion propulsion is more efficient propellant-wise than chemical propulsion but its thrust is very small (around ), thus requires a longer burn time. The thrusters usually use xenon
Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the ...
because it is inert, can be easily ionized
Ionization, or Ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged atom or molecule ...
, has a high atomic mass
The atomic mass (''m''a or ''m'') is the mass of an atom. Although the SI unit of mass is the kilogram (symbol: kg), atomic mass is often expressed in the non-SI unit dalton (symbol: Da) – equivalently, unified atomic mass unit (u). 1&nbs ...
and storable as a high-pressure liquid.
Power
Most satellites usesolar panels
A solar cell panel, solar electric panel, photo-voltaic (PV) module, PV panel or solar panel is an assembly of photovoltaic solar cells mounted in a (usually rectangular) frame, and a neatly organised collection of PV panels is called a phot ...
to generate power, and a few in deep space with limited sunlight use radioisotope thermoelectric generator
A radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG, RITEG), sometimes referred to as a radioisotope power system (RPS), is a type of nuclear battery that uses an array of thermocouples to convert the heat released by the decay of a suitable radioacti ...
s. Slip ring
A slip ring is an electromechanical device that allows the transmission of power and electrical signals from a stationary to a rotating structure. A slip ring can be used in any electromechanical system that requires rotation while transmitting p ...
s attach solar panels to the satellite; the slip rings can rotate to be perpendicular with the sunlight and generate the most power. All satellites with a solar panel must also have batteries, because sunlight is blocked inside the launch vehicle and at night. The most common types of batteries for satellites are lithium-ion
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. It is the predominant battery type used in portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles. It also sees ...
, and in the past nickel–hydrogen.
Communications
*Applications
Earth observation
 Earth observation satellites is designed to monitor and survey the Earth, called
Earth observation satellites is designed to monitor and survey the Earth, called remote sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring information about Earth ...
. Most Earth observation satellites are placed in low Earth orbit for a high data resolution, though some are placed in a geostationary orbit
A geostationary orbit, also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit''Geostationary orbit'' and ''Geosynchronous (equatorial) orbit'' are used somewhat interchangeably in sources. (GEO), is a circular geosynchronous orbit in altitud ...
for an uninterrupted coverage. Some satellites are placed in a Sun-synchronous orbit
A Sun-synchronous orbit (SSO), also called a heliosynchronous orbit, is a nearly polar orbit around a planet, in which the satellite passes over any given point of the planet's surface at the same local mean solar time. More technically, it is ...
to have consistent lighting and obtain a total view of the Earth. Depending on the satellites' functions, they might have a normal camera, radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, w ...
, lidar
Lidar (, also LIDAR, or LiDAR; sometimes LADAR) is a method for determining ranges (variable distance) by targeting an object or a surface with a laser and measuring the time for the reflected light to return to the receiver. It can also be ...
, photometer
A photometer is an instrument that measures the strength of electromagnetic radiation in the range from ultraviolet to infrared and including the visible spectrum. Most photometers convert light into an electric current using a photoresistor, ph ...
, or atmospheric instruments. Earth observation satellite's data is most used in archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
, cartography
Cartography (; from grc, χάρτης , "papyrus, sheet of paper, map"; and , "write") is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an im ...
, environmental monitoring, meteorology, and reconnaissance applications. As of 2021, there are over 950 Earth observation satellites, with the largest number of satellites operated Planet Labs.
Weather satellites monitor clouds, Street light, city lights, fires, effects of pollution, auroral light, auroras, Dust storm, sand and dust storms, snow cover, ice mapping, boundaries of ocean currents, energy flows, etc. Environmental monitoring satellites can detect changes in the Earth's vegetation, atmospheric trace gas content, sea state, ocean color, and ice fields. By monitoring vegetation changes over time, droughts can be monitored by comparing the current vegetation state to its long term average. Anthropogenic emissions can be monitored by evaluating data of tropospheric NO2 and SO2.
Communication
Navigation
Navigational satellites are satellites that use radio time signals transmitted to enable mobile receivers on the ground to determine their exact location. The relatively clear line of sight between the satellites and receivers on the ground, combined with ever-improving electronics, allows satellite navigation systems to measure location to accuracies on the order of a few meters in real timeTelescope
Astronomical satellites are satellites used for observation of distant planets, galaxies, and other outer space objects.
Experimental
Tether satellites are satellites that are connected to another satellite by a thin cable called a tether. Recovery satellites are satellites that provide a recovery of reconnaissance, biological, space-production and other payloads from orbit to Earth. Biosatellites are satellites designed to carry living organisms, generally for scientific experimentation. Space-based solar power satellites are proposed satellites that would collect energy from sunlight and transmit it for use on Earth or other places.Weapon
Since the mid-2000s, satellites have been hacked by militant organizations to broadcast propaganda and to pilfer classified information from military communication networks. For testing purposes, satellites in low earth orbit have been destroyed by ballistic missiles launched from earth. Russia, United States, China and India have demonstrated the ability to eliminate satellites. In 2007, the China, Chinese military shot down an aging weather satellite, followed by the US Navy shooting down a NRO L-21, defunct spy satellite in February 2008. On 18 November 2015, after two failed attempts, Russia successfully carried out a flight test of an anti-satellite missile known as ''A-235 anti-ballistic missile system, Nudol''. On 27 March 2019, India shot down a live test satellite at 300 km altitude in 3 minutes. India became the fourth country to have the capability to destroy live satellites.Pollution and interference
Issues likespace debris
Space debris (also known as space junk, space pollution, space waste, space trash, or space garbage) are defunct human-made objects in space—principally in Earth orbit—which no longer serve a useful function. These include derelict spacecr ...
, radio and light pollution are increasing in magnitude and at the same time lack progress in national or international regulation. Space debris poses dangers to spacecraft (including satellites) in or crossing geocentric orbits and have the potential to drive a Kessler syndrome which could potentially curtail humanity from conducting space endeavors in the future by making such nearly impossible.
With the increase in numbers of satellite constellations, like SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) is an American spacecraft manufacturer, launcher, and a satellite communications corporation headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the stated goal of ...
Starlink
Starlink is a satellite internet constellation operated by SpaceX, providing satellite Internet access coverage to 45 countries. It also aims for global mobile phone service after 2023. SpaceX started launching Starlink satellites in 2019. As ...
, the astronomical community, such as the International Astronomical Union, IAU, report that orbital pollution is getting increased significantly. A report from the SATCON1 workshop in 2020 concluded that the effects of large satellite constellations can severely affect some astronomical research efforts and lists six ways to mitigate harm to astronomy. The IAU is establishing a center (CPS) to coordinate or aggregate measures to mitigate such detrimental effects.
Some notable satellite failures that polluted and dispersed radioactive materials are Kosmos 954, Kosmos 1402 and the List of nuclear power systems in space, Transit 5-BN-3.
Generally liability has been covered by the Liability Convention. Using wood as an alternative material has been posited in order to reduce pollution and debris from satellites that reenter the atmosphere.
Due to the low received signal strength of satellite transmissions, they are prone to Radio jamming, jamming by land-based transmitters. Such jamming is limited to the geographical area within the transmitter's range. GPS satellites are potential targets for jamming, but satellite phone and television signals have also been subjected to jamming.
Also, it is very easy to transmit a carrier radio signal to a geostationary satellite and thus interfere with the legitimate uses of the satellite's transponder. It is common for Earth stations to transmit at the wrong time or on the wrong frequency in commercial satellite space, and dual-illuminate the transponder, rendering the frequency unusable. Satellite operators now have sophisticated monitoring that enables them to pinpoint the source of any carrier and manage the transponder space effectively.
References
External links
*EO Portal directory
{{DEFAULTSORT:Earth Observation Satellite Earth observation satellites, Satellites by type Satellite imagery Satellites, Articles containing video clips Spacecraft Soviet inventions